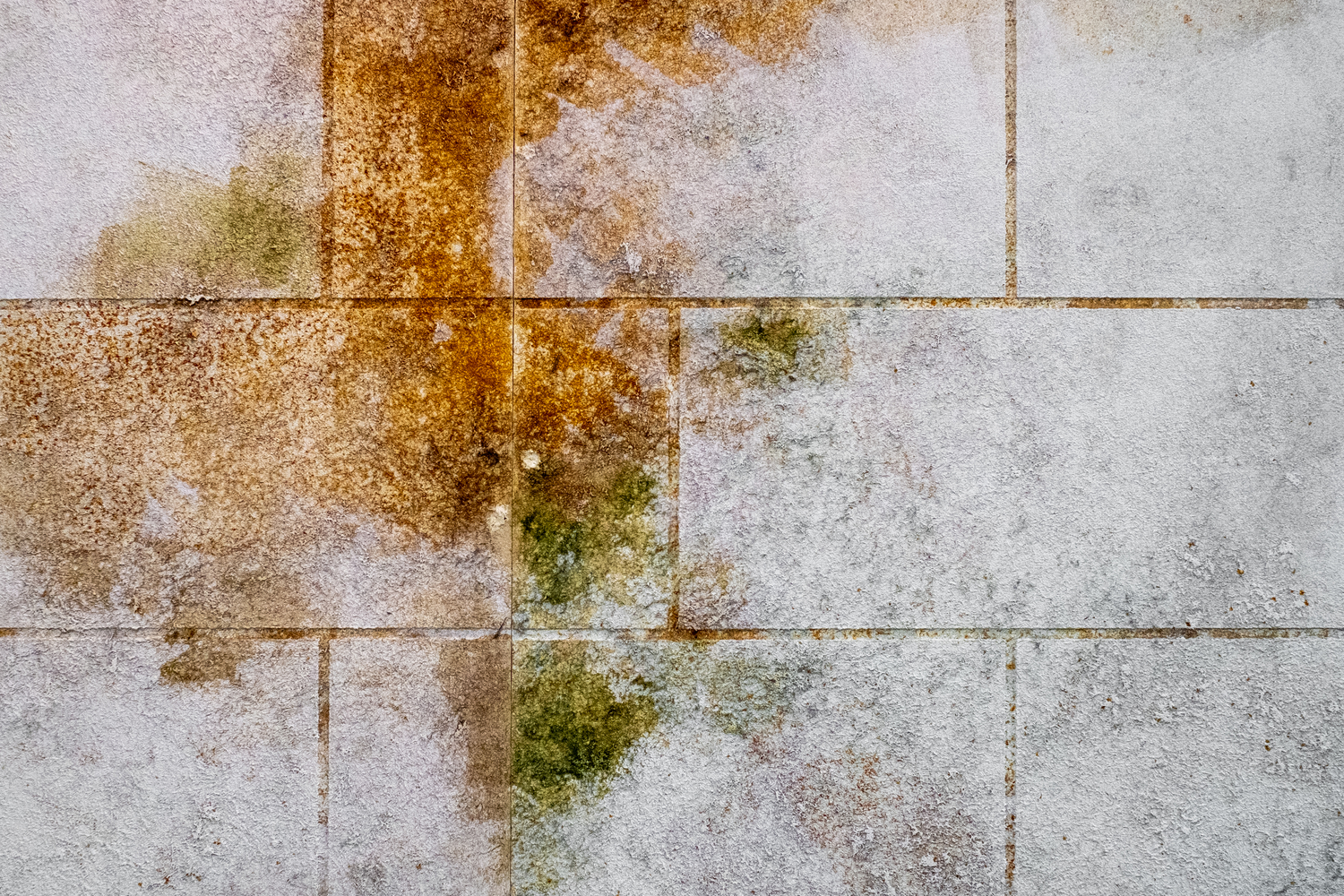
There are many different types of fungi living in the world around us. Some are benign, some are beneficial, and some can be dangerous. We are not talking here about mold on oranges, but orange colored mold. Orange mold is often slimy and spongy instead of fuzzy like most other types of molds, and is capable of growing on foods, wood, and other items. This type of mold will appear as small dark-shaded spots as it begins to grow before assuming its slimy, orange color. It often grows along side and in addition to other types of mold. So, the question is, is it dangerous?
Orange mold is not considered to be a great health threat, but it isn’t completely harmless either. If a person has sensitivities to mold, he or she can still have a negative reaction if exposed to this type of mold.
Mold-Related Health Illnesses
Inhaling or physically contacting mold or mold spores can result in many different allergic reactions. These reactions can be immediate or they can develop over time after lengthy exposure. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that exposure to moldy environments may cause these dangerous health affects:
- Stuffy or Runny Nose
- Wheezing
- Eye and Throat Irritation
- Coughing
- Skin Rash
- Asthma
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
- Lung Irritations
- Acute idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage (bleeding in the lungs)
- Memory Loss
- Lethargy
Common Areas for Orange Mold to Grow
One of the most common places to find orange mold growing is in the kitchen on refrigerated foods. It especially likes dairy products like yogurts and cheeses, and also breads. That is not to say that this mold will not grow outside your refrigerator. It can be found on foods stored in containers or on shelves.
An important thing to remember regarding orange mold contamination is that in can also affect water filters. If your refrigerator has the ability to supply water, either in a glass or an icemaker, its water filter could become contaminated. Check it and replace it at recommended intervals and try to avoid leaving any moldy foods in the refrigerator. Trash them as soon as you discover them as this will keep the mold from spreading to other stored foods. In areas of the country where rainwater contains higher levels of acidity, orange mold may be more common. If you have hard water (no water softener) that is something orange mold is attracted to.
Wood is a favorite food source for orange mold. It can attack windowsills, exposed floor joists in your basement, and in the attic, because attics usually contain warmer air temperatures and moisture or humidity that rises from the rest of your house.
Common Types of Orange Mold
There are four sub-categories for orange mold. Each one has a slightly different appearance and different levels of toxicity.
Acremonium – this mold has little to no affect on people unless their immune systems are weakened in some way. It is a slower growing mold, taking around five days to develop. It appears leathery as it ages. As well as appearing orange, it can also be gray or pinkish in color.
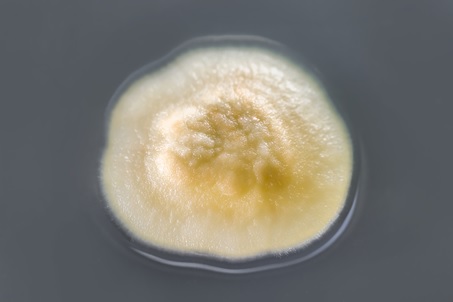
Fuligo Septica – this mold is truly disgusting to look at. Sometimes it is called “dog vomit slime” as that is what it resembles. It is mostly found outdoors and can be orange or yellow in color. As its food or water supply is exhausted, this mold will change its appearance to more closely resemble other molds. It is virtually harmless to humans, although its dusty mold spores can be inhaled and irritate sensitive individuals.

Orange Slime – guess what this mold looks like. Its name says it pretty well. It is also referred to as “sludge mold”. This mold most commonly appears on trees, commonly is considered just an annoyance and is basically harmless to humans.

Aleuria Aurantia – this fungus is easily identified by its orange peel-like appearance. Sometimes it is even called orange peel fungus. It is widespread and is a brilliant orange color. It appears cup or saucer-shaped, looking like a piece of a discarded orange peel. As far as toxicity is concerned, Aleuria mold can be eaten without any harmful effects.

Removing Orange Mold
Depending on where you find this mold, there are several different ways to eliminate it. In your toilet, you can clean the mold with bleach, vinegar, or hydrogen peroxide solutions. Flushing the toilet often will help prevent molds by reducing the microorganism present in the water. A portable steamer is also something that is very effective for removing molds in toilets.
For water filters, changing them on schedule and using an oxidizing filter will help. In your refrigerator, you should discard foods that may become moldy, and then clean the inside surfaces of your refrigerator using the above mentioned bleach, vinegar, or hydrogen peroxide solutions.
If you are trying to remove orange mold from wood, never use bleach. Bleach is made up of chlorine and water, actually most bleach is 96% water. Chlorine is scientifically made to only work on the surface of any material. It will not harm anything growing below the surface (mold has roots). The water in the bleach will soak in though, providing additional water to what you are attempting to kill.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends against attempting removing larger amounts of mold yourself. Any area larger than 10 square feet in size should be remediated by a professional mold removal company. You should never attempt to address any mold problem that may be in your HVAC system.
If you see mold, or think you may have a problem with mold in your home, you should contact Water Mold Fire Restoration at 800-905-0277. We have certified mold remediation experts that can answer any questions you may have about mold and removing mold safely. Our professional remediation teams will effectively eliminate any mold from your home. We answer our phones 24 hours a day, even on holidays. Our initial mold inspection and consultation are free with no obligation. If you would rather contact us by email, do so at help@watermoldfire.net.